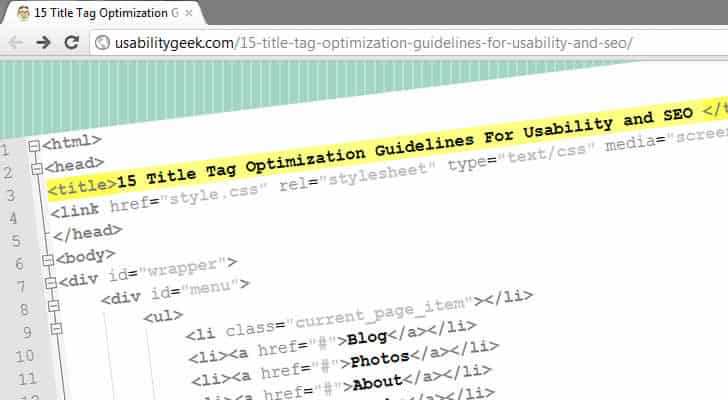
The HTML title tag defines the name of a web page and should be used to describe content of that page in a concise way. Thus, what is placed between the opening and closing HTML title tag is extremely important for both usability and Search Engine Optimization (SEO). In this post I will discuss proven title tag optimization guidelines that you can use to create the ultimate title tag: one that is both human and search engine friendly – a title that will help in driving quality traffic to your web site.
Title Tag Optimization: Why is it important?
Title tag optimization is important because the content of the title tag is used by:
-
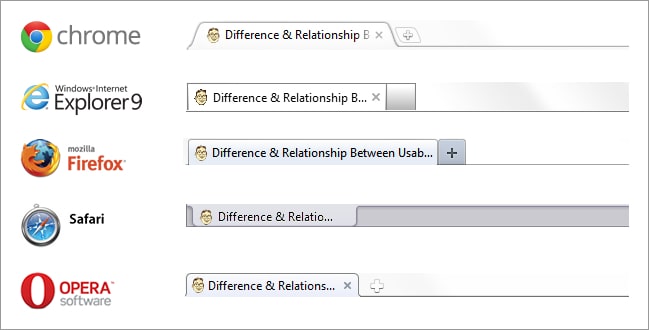
- Web browsers: To label the web browser’s tab(s) (Older browsers used to display the title of the web page in the browser’s window title)
-
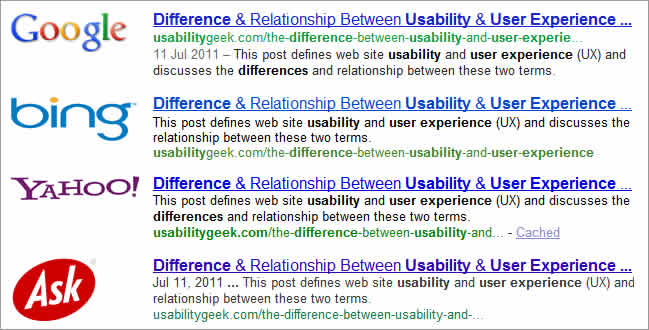
- Search engines: As the clickable headline for listings on Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs)
-
- Search engines: To determine the topic of the web page. Search Engine spiders or crawlers analyze the content of the page title and then translate the page topic.
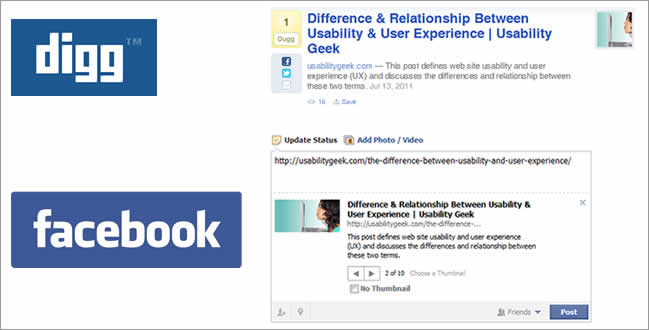
- Social bookmarking sites and Web browsers: To assign a default value to bookmarked web sites
- Users: to
- Identify the web sites that are likely to contain the information they are searching for within the list of web sites on a SERP
- Locate the tab in their web browser which contains the site they want to view
- Find the web site they have bookmarked in their browser
- Determine whether a web site that others have bookmarked in a social bookmarking web site is worth checking out
There is an overlap between usability and Search Engine Optimization as to what techniques can be applied in order to optimize the title of a web page. Thus, I have compiled the following list of guidelines which, if adhered to, will make your web pages both useful and SEO-friendly
Title Tag Optimization: The Do’s
-
- Place your keywords at the beginning: Search engines assign more importance to the first word in the title tag than to the second one and so forth. From a usability perspective, since users understand just the first 11 characters of links, then it is important to make the most out of these characters by placing the most important content there.
- Use keyphrases instead of keywords: If your page title contains a phrase instead of a keyword, then it is more likely that you will attain a higher ranking in search engines for specific user searches. Thus, for example if you have a company that makes toys, then you will rank better if your web page title contains more specific keyphrases rather than just “toys”.
- Use modifiers: In SEO, modifiers are words like “best”, “offers”, “buy”, “cheap” and “reviews”. Users tend to include modifiers in when searching and subsequently when scanning the web pages on a SERP.
- Use numbers: This is purely a usability tip. Users do not typically search for the “50 best button designs for inspiration” but they would rather click on it in a SERP rather than a title that reads “best button design inspiration”. I would dare to add more – they would even prefer to click on it rather than one that reads “best button design inspiration – 50 excellent examples”. Numbers convey meaning to users as to what they should expect to find on a web page and they also serve to attract their attention especially if they are at the beginning of the title.
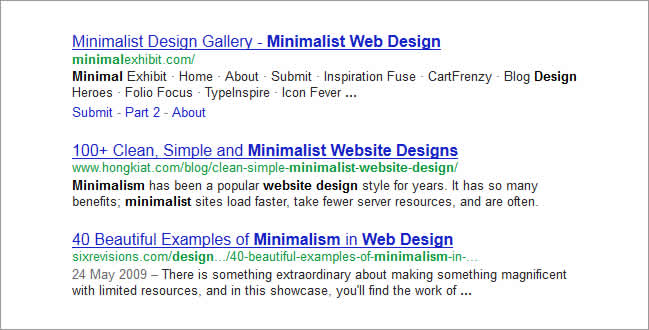
-
- Separate your keywords with hyphens (-) or pipes (|): Both hyphens and pipes will make it easier for your user to scan the content of your title tag. From an SEO perspective, hyphens have the added advantage that they will enable you to rank for different keywords while listing them only once. For example, if you are a web designer, then the keyphrase “web-design” will associate you with search queries for “web design” and “webdesign”. From a usability perspective, this is very useful since you are not restricting the user to type in a specific phrase to reach related content.
- Include Acronyms: Unlike synonyms, there is still some disagreement as on whether search engines interpret the meaning of acronyms. Even if they do, it would be difficult if not impossible for both search engines and users to deduce page content from an acronym alone. This is because acronyms can be interpreted differently like for example “AAA” can be interpreted as American Automobile Association, Access All Areas, Anti Aircraft Artillery and another 190 ways . Still, users may search for the acronym directly (as in the case of SEO). So, if your page content is about something that can be converted to an acronym, it is best to include both the acronym and the full keywords. Acronyms are the only text that should be written in capital case in the title tag. For normal text, use title case or proper case as these are easier to scan and look more professional.
- Each page on your site should have a unique page title: Placing specific keywords in the title tag for each page based on the content of the page will make your individual pages easier to categorize for search engines. Moreover it easier for the user to decide which page to click on in the SERP when presented with a number of pages from your site.
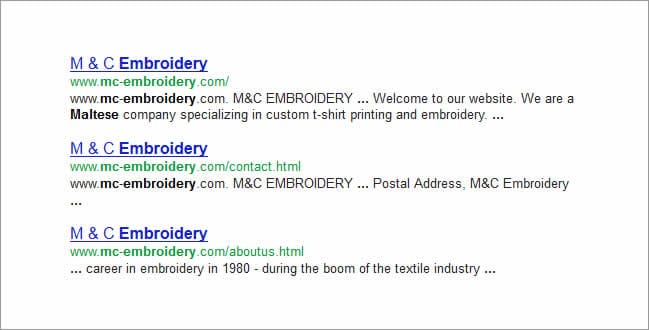
-
- Best title naming convention for the homepage: The first word in the homepage title should be the name of the web site. It should then be followed by the tagline which is a short description of what the web site is about. Never start the title of the homepage with generic words such as “The” or “Welcome” as they would make it more difficult for a user to locate your site. Moreover, if users opt to bookmark it, your site will be indexed under “T”or “W” respectively whereas the user will try and find it using the first character of your company’s name.
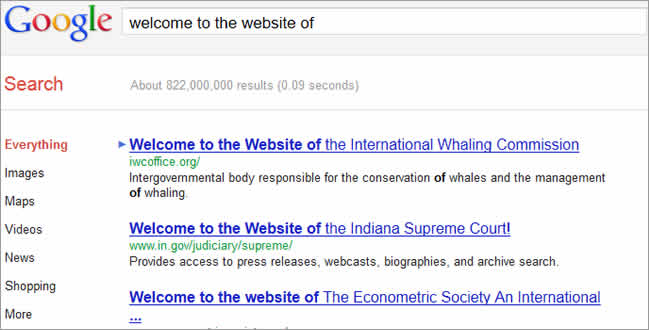
-
- Best title naming convention for other pages: Start the title with the keywords or most prominent information-carrying words that describe what the page contains. These should be followed by the company name at the end of the title. The reason why the company name is placed at the end of the title is that if a user accesses an inner page via it’s home page, then he/she already knows which site they are on. If they access it via a web search, then they are more interested in the specific content of that page. They would still be able to identify who owns the site via the site ID (such as the logo).
Title Tag Optimization: The Don’ts
-
- Do not make the content in the title tag longer than 69 characters: This is because Google, Bing and Ask only show the first 69 characters as the title of web pages in their SERPs whilst Yahoo! shows 72 (source). Still, this does not necessarily mean you have to try and use all 69 characters at your disposal. Whilst more keywords may enable you to show up in more searches, your users will find it more difficult to scan longer page titles. Additionally, because of keyword density , keywords in your title will be more relevant for search engines if your title contains less characters.
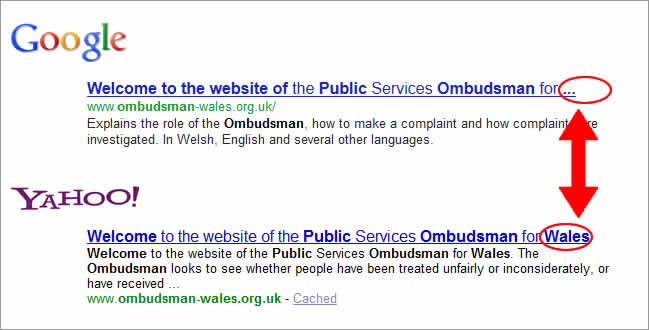
- Do not place too many keywords: From an SEO perspective, this constitutes a practice known as keyword stuffing in order to attain better search rankings. Not only will this technique not work but, major search engines such as Google will penalize you for it. From a usability perspective, even if your page manages to show up on a SERP, it will be unlikely that a user clicks on it for the simple reason that it will look like you have a web page that discusses a little of everything. So, keyword stuffing make your page title look amateurish and will show little value to the user.
- Do not use stop words: Stop words are words that are ignored by search engines and (sometimes) users. These include words such as “by”, “it” and “as”. There are quite a number of stop words so it is worth checking them out when optimizing your title tag. From a usability perspective, I recommend that you do this process carefully. Be judgemental and only remove useless words that do not help the user in identifying your page content. Remember that some users will still include stop words in their search queries.
- Do not use a lot of commas: Whilst commas may look good for the user to scan the content of your page title, using a lot of them may cause search engines to penalize you since they interpret it as keyword stuffing. Thus it is advisable to separate your keywords using the hyphen (-), pipe (|) or underscore (_) symbols. Yes, underscore. Whilst I find the underscore symbol as not very usable, I included it since surprisingly, some “experts” seem to have forgotten that search engines have been treating underscores like hyphens since 2007!
- Do not use special characters: Search engines tend to ignore special characters. For example Google ignores punctuation symbols and other special characters. On the other hand, special characters may be used to attract the user’s attention, although I personally think that such strategy will backfire since it decreases the site’s credibility. Thus it is best to avoid them as they do not add real value to the user or SEO.
- Do not overuse synonyms: It is true that users may use “buy” to mean “purchase” and vice versa so you may be inclined to place them both in your title. Unfortunately, this will cost you the wastage of valuable characters in your title tag. Luckily, search engines such as Google (since 2008) recognise more and more synonyms. So, my advice is to include synonyms only if you think that users may equally search for the different keywords. Otherwise, stick to the most common keyword.
Conclusion
I think that by now you should have a better idea of the importance of the title tag and how to optimize it for both usability and SEO. My final word of advice is that what you would have achieved at this point is a step forward towards making your web pages easier to find and more usable in terms of scannability. However, as the saying goes, “content is king”.
As search engine algorithms evolve, they are able to better detect the content of your pages and they will penalize you in rankings if the content is not of sufficient quality to match the user’s search query. Moreover, if your web page still manages to rank and the user clicks on it because you have a good title, he or she will not hesitate to close the browser tab if they do not see good content within the first 10-20 seconds of scanning its content.
Bottom line is this – Write quality content and then, based on what you write you can optimize the title of that page using the guidelines explained above.
Want to learn more?
Want to get an industry-recognized Course Certificate in UX Design, Design Thinking, UI Design, or another related design topic? Online UX courses from the Interaction Design Foundation can provide you with industry-relevant skills to advance your UX career. For example, Design Thinking, Become a UX Designer from Scratch, Conducting Usability Testing or User Research – Methods and Best Practices are some of the most popular courses. Good luck on your learning journey!
